These are coffee beans coated in a sugar-based candy shell. The confection provides a textural contrast between the crisp, sweet exterior and the bitter, robust interior of the coffee bean. The coating process involves applying a sugar syrup to the beans, often followed by drying and crystallization, resulting in a hard, protective layer. As an example, commercially available products are often sold as impulse buys or specialty coffee treats.
The value of this specific confectionery lies in its dual functionality. It serves as both a stimulant, owing to the caffeine content, and a sweet treat, satisfying cravings. Historically, similar techniques of preserving or enhancing the flavor of food items through sugar coatings have been prevalent across various cultures. In modern contexts, these coated beans are also viewed as a convenient and palatable way to consume coffee, particularly for individuals who prefer a less intense coffee flavor.
The following article will explore the preparation methods, flavor variations, commercial availability, and potential health considerations associated with this unique type of candy. Subsequent sections will also delve into the sensory experience and consumer appeal contributing to its popularity.
Tips for Working with Candied Coffee Beans
The following offers practical guidance for those interested in incorporating candied coffee beans into culinary applications or simply seeking to maximize their enjoyment of the product.
Tip 1: Storage Considerations: To maintain optimal texture and prevent the candy coating from becoming sticky, store the beans in an airtight container in a cool, dry place. Avoid refrigeration, as condensation can negatively affect the candy shell.
Tip 2: Incorporating into Recipes: When adding the beans to baked goods or desserts, consider coarsely chopping them to evenly distribute the flavor and texture. This prevents large pieces from dominating a single bite.
Tip 3: Controlling Caffeine Intake: Be mindful of the caffeine content, especially when consuming multiple beans. Individuals sensitive to caffeine should exercise moderation to avoid unwanted side effects.
Tip 4: Pairing with Flavors: Experiment with complementary flavors such as chocolate, nuts, and spices to enhance the overall taste profile. The bitterness of the coffee bean pairs well with sweet and nutty elements.
Tip 5: Understanding Coating Variations: Recognize that different manufacturers use varying coating techniques and ingredients. This can result in significant differences in sweetness, texture, and overall flavor. Read product labels carefully to make informed choices.
Tip 6: Utilizing in Coffee Blends: Add a small quantity of coarsely crushed candied coffee beans to ground coffee before brewing. This can subtly infuse the beverage with a hint of sweetness and caramelization.
Effective utilization of these tips will contribute to a more informed and enjoyable experience when using or consuming candied coffee beans.
The subsequent section will address potential health considerations related to the consumption of this particular confection.
1. Sweetness Intensity
The degree of sweetness in sugar-coated coffee beans fundamentally determines its consumer appeal and overall flavor profile. The interaction between the inherent bitterness of the coffee bean and the added sugar creates a balance that dictates whether the product is perceived as a palatable treat or an overly saccharine confection. Variations in sweetness intensity can be achieved through manipulating the ratio of sugar to coffee bean, the type of sugar used (e.g., granulated sugar, brown sugar, honey), and the thickness of the coating. For instance, a lightly sweetened variant might appeal to coffee purists seeking a subtle enhancement, whereas a heavily coated version caters to those with a stronger preference for sweet flavors.
The significance of sweetness intensity extends beyond mere taste preferences. It influences the product’s market positioning and target demographic. Lower sweetness levels can align the product with health-conscious consumers, while higher sweetness levels may attract a younger audience. In practical application, producers carefully calibrate sweetness levels based on market research and consumer feedback, adjusting their formulas to achieve optimal market penetration. Furthermore, sweetness intensity affects the overall sensory experience, influencing the perception of other flavors and textures. An excessively sweet coating can mask the nuanced flavors of the coffee bean, while an insufficient level may fail to provide the desired counterpoint to the bean’s bitterness.
In conclusion, the proper management of sweetness intensity is paramount to creating a successful product. Balancing the bitter and sweet components is a delicate art that requires a comprehensive understanding of consumer preferences, market trends, and the inherent properties of both the coffee bean and the sugar coating. The failure to achieve this balance can result in a product that is either unpalatable or fails to differentiate itself in a competitive marketplace. Achieving the optimal sweetness level, therefore, constitutes a critical challenge for producers.
2. Bean Origin
The geographic origin of coffee beans significantly impacts the final flavor profile and characteristics of the product. The terroir, encompassing soil composition, climate, and altitude, imparts unique qualities to the bean that can either complement or clash with the added sweetness of the candy coating. Selecting an appropriate bean origin is, therefore, a critical step in the creation of a harmonious and flavorful confection.
- Acidity and Brightness
Beans from East Africa, such as Ethiopia and Kenya, are often characterized by high acidity and bright, fruity notes. When these beans are candied, the sweetness can accentuate the natural fruitiness, creating a complex and vibrant flavor. However, if the sugar coating is too intense, it can overwhelm the delicate acidity, resulting in a cloying sweetness. Producers must carefully balance the sweetness to allow the inherent qualities of the bean to shine through.
- Body and Nutty Flavors
South American beans, particularly those from Brazil, are known for their medium body and nutty, chocolatey undertones. The candy coating can enhance these flavors, creating a comforting and familiar taste. However, the choice of coating matters; a dark chocolate coating may complement the inherent chocolate notes of the bean, while a vanilla-flavored coating could create an undesirable clash. The producer must consider these interactions carefully.
- Earthy and Herbal Notes
Sumatran or Indonesian beans often exhibit earthy and herbal characteristics. These beans, when candied, present a unique challenge. The sweetness can soften the earthiness, making the beans more palatable to a wider audience. However, an overly sweet coating can mask the complexity and subtlety of the herbal notes, resulting in a less nuanced product. The goal is to enhance, not eradicate, the original flavor profile.
- Roast Level Considerations
Regardless of origin, the roast level also plays a crucial role. A lightly roasted bean will retain more of its original characteristics, while a dark roast will impart smoky or bitter notes. When combining origin and roast, a lightly roasted East African bean might pair well with a delicate sugar coating, while a dark-roasted Indonesian bean could benefit from a slightly bolder, more intense sweetness to counterbalance the bitterness.
In conclusion, the origin of the coffee beans profoundly affects the flavor profile of the final product. Producers must meticulously consider the inherent characteristics of each bean, carefully selecting a coating and roast level that enhances, rather than obscures, the bean’s natural qualities. The success of a candied coffee bean depends not only on the sweetness of the coating, but also on the harmonious interplay between the origin of the bean and the added sugar.
3. Coating Texture
The texture of the coating on these beans is paramount to the overall sensory experience and directly influences consumer perception. A coating that is too hard may be difficult to bite through, leading to an unpleasant experience. Conversely, a coating that is too soft can become sticky, diminish the structural integrity of the product, and compromise shelf life. The ideal texture balances initial crispness with a satisfying melt-in-the-mouth quality. For example, a smooth, uniform coating achieved through pan-coating techniques offers a consistent and appealing texture compared to a rough, uneven coating resulting from less controlled methods. Consider commercial examples where inconsistent coating leads to consumer dissatisfaction, often expressed in negative product reviews and reduced sales.
Various factors contribute to the ultimate coating texture, including the type of sugar used, the syrup concentration, the coating application method, and the environmental conditions during drying. For example, using high-fructose corn syrup can result in a softer, chewier coating, while using crystalline sugar creates a firmer, snappier texture. The application method, whether through panning, dipping, or spraying, affects the uniformity and thickness of the coating. Proper temperature and humidity control during the drying process are essential to prevent stickiness and ensure proper crystallization. Understanding these variables allows producers to fine-tune their processes to achieve the desired textural characteristics. In practical applications, manufacturers employ various testing methods, such as texture analyzers, to objectively measure and control coating hardness, crispness, and adhesiveness, ensuring product consistency.
In summary, the coating texture is not merely a superficial aspect; it is a fundamental determinant of the product’s quality and appeal. Achieving the optimal texture requires careful selection of ingredients, precise control of the coating process, and a thorough understanding of the underlying principles of sugar crystallization. The challenges lie in maintaining consistency across large-scale production and adapting to varying environmental conditions. Ultimately, a well-executed coating texture enhances the enjoyment and value of the product, contributing significantly to its success in the marketplace.
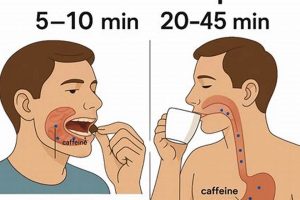
4. Caffeine Content
The caffeine content within sugar-coated coffee beans represents a significant consideration for consumers and manufacturers alike. Its presence defines the product’s stimulant properties and directly influences its appeal, potential health effects, and regulatory considerations.
- Dosage Control
The caffeine dose delivered by sugar-coated coffee beans is inherently variable, dependent on bean size, coffee variety (Arabica vs. Robusta), roast level, and the number of beans consumed. Unlike standardized caffeine sources such as energy drinks, the exact caffeine intake from these beans is difficult to ascertain without specific product testing. Individuals sensitive to caffeine must exercise caution, given the potential for inadvertent overconsumption. This variability necessitates clear labeling practices to inform consumers about potential caffeine levels per serving.
- Stimulant Effects
The caffeine within the candy elicits typical stimulant effects, including increased alertness, reduced fatigue, and enhanced cognitive function. These effects can be desirable for some consumers seeking a quick energy boost. However, excessive caffeine consumption can lead to adverse effects, such as anxiety, insomnia, and heart palpitations. The combined effects of sugar and caffeine may also lead to a more pronounced “crash” following the initial stimulation, potentially discouraging repeated consumption. Producers must consider these effects when marketing the product.
- Interaction with Sugar
The combination of caffeine and sugar in this confectionery can create a synergistic effect. Sugar provides a rapid source of energy, while caffeine enhances alertness. This combination can be particularly appealing but may also contribute to a cycle of sugar highs and lows, potentially leading to cravings and overconsumption. This interaction necessitates mindful consumption, especially for individuals managing blood sugar levels or seeking sustained energy without subsequent crashes.
- Regulatory Landscape
The caffeine content influences how these coated beans are categorized and regulated. Products exceeding a certain caffeine level may be subject to specific labeling requirements or restrictions, depending on the jurisdiction. Manufacturers must comply with these regulations to ensure legal market access. Furthermore, the potential for misinterpreting these candies as simple sweets, particularly by children, has prompted scrutiny from regulatory bodies, emphasizing the need for responsible marketing practices and clear warnings about caffeine content.
The interplay between caffeine and the candy matrix presents both opportunities and challenges. While the stimulant properties can enhance the product’s appeal, potential health effects and regulatory considerations necessitate careful management. Clear labeling, responsible marketing, and a focus on dosage control are essential for ensuring consumer safety and sustaining long-term market viability.
5. Shelf Life
The duration for which sugar-coated coffee beans maintain acceptable quality represents a critical factor influencing production, distribution, and consumer satisfaction. Understanding the mechanisms governing degradation and implementing appropriate preservation strategies are essential for maximizing the lifespan of this product. Shelf life directly affects economic viability and market reach.
- Moisture Content
The water activity within and surrounding the beans is a primary determinant of shelf stability. Excessive moisture promotes microbial growth, particularly mold, leading to spoilage and rendering the product unsafe for consumption. Furthermore, elevated moisture levels can cause the sugar coating to dissolve or become sticky, altering the texture and appearance. Proper drying techniques and the use of moisture-barrier packaging are critical for minimizing water activity and extending shelf life. For example, improperly dried beans stored in non-airtight containers will deteriorate rapidly.
- Lipid Oxidation
Coffee beans contain unsaturated fats that are susceptible to oxidation, especially when exposed to oxygen, light, and heat. Oxidative rancidity results in off-flavors and aromas, diminishing the sensory quality of the confection. Antioxidants, such as vitamin E, may be incorporated into the coating to mitigate lipid oxidation. Furthermore, packaging materials with oxygen barrier properties, such as metallized films, can help to reduce oxygen exposure. Real-world examples demonstrate that beans stored under vacuum or nitrogen-flushed environments exhibit significantly prolonged shelf life compared to those stored in open air.
- Sugar Crystallization
The stability of the sugar coating itself is crucial for maintaining product integrity. Changes in temperature and humidity can induce sugar crystallization, leading to a grainy or sandy texture on the surface. This phenomenon, known as sugar bloom, does not necessarily render the product unsafe but detracts from its aesthetic appeal and perceived quality. Formulating the coating with invert sugars or using a combination of different sugar types can help to inhibit crystallization. Proper storage conditions, such as maintaining a stable temperature and avoiding excessive humidity fluctuations, are essential for preventing sugar bloom.
- Packaging Integrity
The packaging material serves as the primary barrier against environmental factors that contribute to degradation. Packaging should provide adequate protection against moisture, oxygen, light, and physical damage. Airtight containers, sealed bags, and properly labeled packaging are essential for communicating storage instructions to consumers. Compromised packaging can accelerate spoilage and render the product unmarketable. As an example, products packaged in flimsy or damaged containers often exhibit reduced shelf life and increased rates of consumer complaints.
The interplay of moisture control, lipid oxidation mitigation, sugar crystallization prevention, and maintenance of packaging integrity collectively determines the viable shelf life of the final product. Careful attention to each of these factors is crucial for ensuring consumer satisfaction and minimizing economic losses associated with spoilage. Manufacturers must conduct rigorous shelf-life studies under various storage conditions to establish appropriate expiration dates and provide accurate storage instructions to consumers. Optimizing these parameters is vital for sustaining market competitiveness.
6. Flavor Pairings
The intentional pairing of complementary tastes and aromas with sugar-coated coffee beans directly impacts the sensory experience and market appeal. The inherent bitterness and roasted notes of the coffee bean create a foundation upon which additional flavors can be layered. The selection of appropriate flavor pairings becomes a pivotal factor in determining the product’s perceived value and target audience. For instance, combining dark chocolate with deeply roasted beans amplifies the existing chocolate notes, creating a familiar and satisfying experience. Conversely, pairing a citrus flavor with a lighter roast can highlight the bean’s acidity, resulting in a more vibrant and refreshing product. In both instances, the intentional pairing elevates the overall experience beyond simply masking the bitterness.
Practical application of this understanding manifests in various product offerings. Some manufacturers experiment with spices such as cinnamon or cardamom to introduce warmth and complexity, appealing to consumers seeking adventurous flavor profiles. Others focus on nut-based pairings, such as almond or hazelnut, to complement the natural nutty undertones of certain bean origins. Furthermore, the sugar coating itself can be infused with flavors, allowing for greater control over the final taste. A caramel-flavored coating, for example, can add a layer of sweetness and depth that enhances the coffee bean’s natural characteristics. The key lies in achieving a balance where the added flavor enhances, rather than overpowers, the inherent qualities of the coffee bean. Real-world examples demonstrate the commercial success of well-executed flavor pairings, leading to increased sales and brand recognition. Conversely, poorly conceived pairings can result in consumer dissatisfaction and product rejection.
In summary, strategic flavor pairings represent a crucial element in the production and marketing. The careful selection of complementary flavors enhances the sensory experience, broadens market appeal, and differentiates products in a competitive landscape. While challenges exist in predicting consumer preferences and achieving flavor balance, the potential rewards, in terms of increased sales and brand loyalty, justify the effort invested in this aspect of product development. Ultimately, a deep understanding of flavor interactions allows manufacturers to transform a simple sugar-coated coffee bean into a sophisticated and desirable treat.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries and clarifies misconceptions surrounding coffee beans coated in a sugar shell.
Question 1: What is the typical caffeine content in a serving?
The quantity varies considerably based on bean size, coffee variety (e.g., Arabica, Robusta), and roast level. A single serving (approximately 1 ounce) can contain anywhere from 30mg to over 100mg of caffeine. Labels should be consulted to determine specific caffeine levels.
Question 2: Are there any potential health risks associated with consuming this product?
Consumption should be moderated due to the combined effects of caffeine and sugar. Excessive intake may lead to anxiety, insomnia, increased heart rate, and blood sugar fluctuations. Individuals with pre-existing health conditions should consult with a healthcare professional.
Question 3: How should this product be stored to maintain optimal quality?
Optimal storage requires an airtight container in a cool, dry place. Exposure to moisture and heat can degrade the sugar coating and compromise the flavor. Refrigeration is generally not recommended due to condensation.
Question 4: Are there different varieties available?
Varieties exist based on coffee bean origin, roast level, sugar coating type (e.g., dark chocolate, caramel), and added flavorings (e.g., spices, nuts). The specific options available depend on the manufacturer.
Question 5: Are these coated beans suitable for individuals with diabetes?
Due to the high sugar content, consumption should be carefully managed by individuals with diabetes. Portion control is essential, and consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is advisable.
Question 6: Can these candied beans be used in cooking or baking?
These coated beans can be incorporated into culinary applications. Chopping them coarsely and adding them to baked goods or desserts can impart both flavor and texture. However, the added sugar content should be considered when adjusting other recipe ingredients.
Understanding the caffeine content, potential health risks, and proper storage techniques ensures responsible consumption and enjoyment. Varieties exist to cater to different taste preferences, but moderation remains key.
The subsequent section will address the history and cultural significance associated with this particular type of confectionery.
Conclusion
This article has explored various aspects, from their preparation and flavor profiles to health considerations and storage techniques. The analysis encompassed the selection of beans based on origin, the influence of coating texture, and the critical role of caffeine content. Considerations for shelf life and optimal flavor pairings were also examined. These factors collectively determine the quality, appeal, and consumer perception of the final product.
Continued research into innovative coating techniques and flavor combinations may lead to new and exciting variations. Manufacturers are encouraged to prioritize clear labeling practices and responsible marketing strategies, ensuring consumer awareness of both the stimulating effects and potential health implications. Ultimately, the future of this confectionery depends on a commitment to quality, transparency, and a nuanced understanding of consumer preferences.