This beverage is a variation on the popular “bulletproof coffee” concept, distinguished by the inclusion of a specific dairy product known for its high fat content. The typical preparation involves blending hot coffee with this dairy component and a source of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), often in the form of MCT oil. The resulting emulsification creates a creamy, latte-like drink.
The consumption of this high-fat coffee drink is often associated with individuals adhering to ketogenic or low-carbohydrate diets. Proponents suggest potential benefits such as sustained energy levels, increased satiety, and improved mental clarity. The historical context finds its roots in the broader movement toward biohacking and optimizing dietary intake for perceived cognitive and physical advantages.
The subsequent sections will delve into the specific composition of this coffee variant, explore its purported metabolic effects, examine potential drawbacks, and provide guidance on safe and effective preparation methods.
Tips for Optimizing the Consumption of the High-Fat Coffee Beverage
The following recommendations aim to maximize potential benefits and minimize possible adverse effects when incorporating this high-fat coffee into one’s dietary regimen.
Tip 1: Prioritize Ingredient Quality. Selection of high-quality coffee beans and grass-fed, organic heavy cream is crucial. This minimizes exposure to potential toxins and optimizes the nutritional profile of the beverage.
Tip 2: Introduce Gradually. Start with small amounts of heavy cream (e.g., one tablespoon) and gradually increase to assess individual tolerance and minimize potential digestive distress.
Tip 3: Monitor Caloric Intake. Due to its high fat content, this beverage is calorie-dense. Careful monitoring of overall caloric intake is essential to prevent unintended weight gain.
Tip 4: Consider Timing. Consuming this beverage in the morning may provide sustained energy. However, avoid late-day consumption to prevent potential sleep disturbances.
Tip 5: Blend Thoroughly. Proper blending ensures adequate emulsification of the ingredients, enhancing palatability and potentially improving digestion.
Tip 6: Limit Additives. Avoid excessive use of artificial sweeteners or flavorings. If desired, opt for natural alternatives like stevia or a small amount of pure vanilla extract.
Tip 7: Hydrate Adequately. The diuretic effect of coffee may lead to dehydration. Ensure sufficient water intake throughout the day.
The successful integration of this high-fat coffee drink hinges on meticulous preparation and attentive monitoring of individual responses. By adhering to these guidelines, potential benefits may be realized while mitigating risks.
The subsequent section will address common misconceptions and potential controversies associated with this increasingly popular beverage.
1. Satiety
The high fat content inherent in heavy cream significantly contributes to the satiety experienced after consuming this beverage. Fats, in general, elicit a greater release of satiety hormones, such as cholecystokinin (CCK) and peptide YY (PYY), compared to carbohydrates or proteins. These hormones signal to the brain that the body is nourished, reducing appetite and delaying subsequent hunger pangs. The addition of heavy cream to coffee, therefore, transforms a typically less satiating beverage into one capable of suppressing hunger for an extended period.
The practical significance of this heightened satiety lies in its potential to support weight management efforts. Individuals seeking to reduce caloric intake may find that incorporating this coffee variant into their breakfast routine allows them to comfortably extend the time between meals, thereby decreasing overall food consumption. Consider, for example, a person who typically consumes a mid-morning snack due to hunger. Replacing their regular breakfast with this beverage could eliminate the need for the snack, resulting in a reduction in daily caloric intake. However, this strategy necessitates careful consideration of the beverage’s high caloric density and its impact on overall macronutrient balance.
Despite the potential benefits, challenges remain. Individual responses to the beverage’s satiety effects can vary depending on factors such as metabolic rate, activity level, and pre-existing dietary habits. Moreover, relying solely on this beverage for satiety may inadvertently lead to nutrient deficiencies if not balanced with a nutrient-rich diet. The successful implementation of this strategy requires a comprehensive understanding of individual needs and a commitment to mindful eating practices, aligning with broader goals of health and well-being.
2. Ketogenesis
Ketogenesis, the metabolic process of producing ketone bodies from fat, is a central concept in understanding the effects of high-fat dietary interventions, including the consumption of coffee preparations incorporating heavy cream. This process becomes particularly relevant when carbohydrate intake is restricted, forcing the body to seek alternative fuel sources.
- Fatty Acid Oxidation
Ketogenesis is directly dependent on the availability of fatty acids, derived either from dietary fat or from stored body fat. The heavy cream component provides a readily accessible source of saturated fat, which is subsequently broken down through beta-oxidation in the liver. This process yields acetyl-CoA, a precursor to ketone body synthesis. For example, an individual consuming a traditional breakfast high in carbohydrates would primarily utilize glucose for energy, suppressing ketogenesis. In contrast, the consumption of coffee with heavy cream promotes the oxidation of fatty acids and subsequent ketone body production.
- Hormonal Influence
The hormonal milieu plays a critical role in regulating ketogenesis. Insulin, a hormone secreted in response to carbohydrate consumption, inhibits lipolysis (the breakdown of fat) and ketogenesis. Conversely, low-carbohydrate diets and fasting states result in lower insulin levels and elevated levels of glucagon, a hormone that promotes lipolysis and ketogenesis. Thus, the low-carbohydrate nature of the coffee, combined with the fat content of the heavy cream, synergistically supports ketogenesis.
- Ketone Body Utilization
The ketone bodies produced during ketogenesis, primarily acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone, serve as alternative fuel sources for various tissues, including the brain. The brain, which typically relies on glucose for energy, can adapt to utilize ketone bodies under conditions of glucose scarcity. This adaptation is often cited as a potential benefit of ketogenic diets and, by extension, the consumption of high-fat coffee. However, the efficiency of ketone body utilization varies between individuals and depends on factors such as the degree of ketoadaptation and overall metabolic health.
- Potential Side Effects
While ketogenesis can offer potential metabolic benefits, it is also associated with potential side effects, particularly during the initial adaptation phase. The “keto flu,” characterized by symptoms such as fatigue, headache, and nausea, can occur as the body adjusts to utilizing ketone bodies for energy. Additionally, elevated ketone levels can alter electrolyte balance and potentially impact kidney function. Therefore, individuals considering incorporating this coffee beverage as a means of promoting ketogenesis should be aware of these potential drawbacks and consult with a healthcare professional.
The interplay between fatty acid oxidation, hormonal influences, ketone body utilization, and potential side effects underscores the complex relationship between this beverage and ketogenesis. While the coffee may promote ketone body production, its impact on overall metabolic health is contingent on individual factors, dietary context, and careful monitoring of potential adverse effects.
3. Energy Levels
The consumption of coffee incorporating heavy cream is frequently associated with sustained energy levels. This perception stems from the combined effects of caffeine and the metabolic properties of fats, each influencing energy production and utilization within the body. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for evaluating the validity and potential benefits of this practice.
- Caffeine’s Stimulatory Effect
Caffeine, a known stimulant present in coffee, exerts its effects by blocking adenosine receptors in the brain. Adenosine is a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and drowsiness. By inhibiting adenosine, caffeine enhances alertness, reduces perceived fatigue, and increases mental focus. The rapid absorption of caffeine after coffee consumption results in a prompt elevation in energy levels, often characterized by increased wakefulness and cognitive performance. For instance, individuals experiencing morning grogginess may find that caffeine ingestion provides a temporary boost in energy and concentration.
- Sustained Energy from Fat Metabolism
Heavy cream, composed primarily of saturated fat, provides a slow-releasing energy source compared to carbohydrates. Fats are metabolized through beta-oxidation, a process that yields a significant amount of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy currency of cells. Unlike glucose, which can be rapidly utilized and depleted, fats offer a more sustained release of energy, preventing abrupt crashes in blood sugar and energy levels. An athlete, for example, may benefit from the sustained energy provided by fat metabolism during prolonged endurance activities.
- Modulation of Blood Sugar
The presence of fat in coffee consumption can mitigate the rapid rise in blood sugar that typically follows the ingestion of carbohydrates. This is due to the slowing effect of fat on gastric emptying and glucose absorption. Stabilizing blood sugar levels contributes to more consistent energy levels throughout the day, preventing energy fluctuations associated with the consumption of high-carbohydrate foods. Individuals prone to postprandial fatigue may experience improved energy stability when consuming coffee with heavy cream instead of carbohydrate-rich breakfast options.
- Individual Variability
The impact of this beverage on energy levels is subject to considerable individual variability. Factors such as caffeine sensitivity, metabolic rate, pre-existing health conditions, and dietary habits can influence the subjective experience of energy. Some individuals may experience a significant boost in energy and focus, while others may be more susceptible to adverse effects such as anxiety, jitters, or digestive discomfort. Therefore, the effectiveness of the beverage as an energy enhancer is contingent upon individual tolerance and careful self-monitoring.
The combined effects of caffeine and fat metabolism contribute to the perception of sustained energy levels associated with coffee containing heavy cream. However, the magnitude and nature of this effect are dependent on individual factors and require a nuanced understanding of metabolic processes.
4. Cream Quality
The quality of the heavy cream used in coffee directly influences the nutritional profile, flavor, and potential health impacts of the resulting beverage. Heavy cream derived from grass-fed cows, for instance, exhibits a different fatty acid composition compared to that from conventionally raised animals. Grass-fed dairy products tend to contain a higher proportion of omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), both of which are associated with potential health benefits. Therefore, selecting a higher-quality heavy cream can enhance the nutritional value of the coffee.
Beyond nutritional aspects, cream quality significantly affects the sensory experience. Premium heavy cream often boasts a richer, more complex flavor profile and a smoother texture, contributing to a more palatable and satisfying beverage. For example, using ultra-pasteurized cream, while convenient, may result in a less desirable taste compared to non-ultra-pasteurized options, as the high-heat treatment can alter the cream’s flavor compounds. The sourcing and processing methods of the cream are, therefore, critical determinants of the coffee’s overall taste and mouthfeel. The origin of the milk also makes a big difference in the quality of cream.
Ultimately, the choice of heavy cream influences not only the immediate enjoyment of the beverage but also its potential long-term effects on health and well-being. While the addition of any heavy cream will increase the fat content, opting for high-quality, responsibly sourced cream maximizes potential benefits and minimizes exposure to undesirable additives or processing byproducts. The understanding of this interplay between cream quality and the overall composition of the coffee is vital for individuals seeking to optimize their dietary choices.
5. Digestive Impact
The consumption of a high-fat beverage, like coffee prepared with heavy cream, exerts a notable influence on the digestive system. The high fat content can slow gastric emptying, thereby affecting the rate at which nutrients are released into the small intestine. This slower transit time can lead to a feeling of fullness and prolonged satiety, as previously mentioned. However, for individuals with pre-existing digestive sensitivities, this delayed gastric emptying can also manifest as bloating, nausea, or abdominal discomfort. For instance, individuals with a history of gastroparesis, a condition characterized by delayed gastric emptying, may experience exacerbated symptoms after consuming this beverage. The composition of the gut microbiota also plays a role, as different bacterial species metabolize fats in varying ways, potentially leading to gas production or altered bowel habits in certain individuals.
Furthermore, the type of fat present in the heavy cream contributes to its digestive impact. Saturated fats, the predominant type found in heavy cream, are generally more difficult to digest than unsaturated fats. Individuals lacking sufficient lipase, the enzyme responsible for fat digestion, may experience steatorrhea, characterized by the presence of undigested fat in the stool. The quantity of heavy cream consumed is also a critical determinant. A small amount may be well-tolerated, while a larger quantity can overwhelm the digestive system’s capacity, resulting in adverse effects. Consider a scenario where an individual accustomed to a low-fat diet suddenly incorporates a large quantity of high-fat coffee; digestive distress is a likely consequence. Proper emulsification through blending, as highlighted previously, can aid in digestion by reducing the size of fat globules, thereby increasing the surface area available for enzymatic breakdown. The addition of MCT oil may have adverse effects as well.
In summary, the digestive impact of coffee prepared with heavy cream is multifaceted and dependent on individual factors such as pre-existing digestive conditions, enzyme production, and gut microbiota composition, as well as beverage-specific factors such as fat content, type of fat, and emulsification. Careful consideration of these elements is essential for optimizing digestive tolerance and minimizing potential adverse effects. Monitoring individual responses and adjusting the quantity and frequency of consumption accordingly is paramount. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the long-term effects of regularly consuming this high-fat beverage on the digestive system.
6. Caloric Load
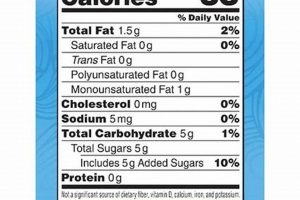
The incorporation of heavy cream into coffee significantly elevates the beverage’s caloric density, transforming it from a relatively low-calorie drink into a potentially substantial source of energy. This elevated caloric load stems primarily from the high fat content of heavy cream, which provides approximately nine calories per gram, compared to four calories per gram for carbohydrates and proteins. Consequently, even a small amount of heavy cream can contribute a significant number of calories to the daily intake. The cause-and-effect relationship is direct: the more heavy cream added, the higher the caloric load becomes. For individuals monitoring their energy intake for weight management or other health-related reasons, this caloric load necessitates careful consideration.
The importance of understanding the caloric load of coffee prepared with heavy cream lies in its potential to disrupt energy balance. If an individual consumes this beverage regularly without adjusting other dietary components, a caloric surplus may result, leading to weight gain over time. For example, replacing a zero-calorie black coffee with a version containing two tablespoons of heavy cream (approximately 100-200 calories) can add a substantial number of calories to a daily routine. The practical significance of this understanding is that it empowers individuals to make informed choices about their dietary habits, balancing the perceived benefits of the beverage with its potential impact on their overall health. Those following ketogenic diets may find the high-fat, low-carbohydrate nature of the beverage suitable, yet the caloric load still necessitates monitoring to maintain ketosis and achieve desired outcomes.
In conclusion, the caloric load associated with coffee prepared with heavy cream is a critical factor to consider when evaluating its place in a balanced diet. While the beverage may offer potential benefits related to satiety and energy levels, its high caloric density warrants careful monitoring to prevent unintended consequences such as weight gain. Balancing the consumption of this beverage with other dietary choices and adjusting overall caloric intake accordingly is essential for achieving optimal health outcomes. The challenge lies in integrating this high-calorie drink into a holistic dietary plan that supports individual needs and goals.
Frequently Asked Questions About Heavy Cream Bulletproof Coffee
The following questions address common inquiries and misconceptions regarding the consumption of coffee prepared with heavy cream, providing evidence-based insights to inform decision-making.
Question 1: Is daily consumption of coffee prepared with heavy cream detrimental to cardiovascular health?
The impact on cardiovascular health is complex and depends on individual factors, including pre-existing conditions and overall dietary patterns. While heavy cream contains saturated fat, which has historically been linked to increased LDL cholesterol, recent research suggests that the effect of saturated fat on cardiovascular risk may be more nuanced than previously understood. Moderation and consideration of total dietary fat intake are advised. Individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions should consult with a healthcare professional.
Question 2: Does coffee prepared with heavy cream promote weight loss?
The high fat content may promote satiety, potentially reducing overall caloric intake. However, due to its high caloric density, this beverage can contribute to weight gain if not balanced with other dietary adjustments. A comprehensive weight management strategy, including regular physical activity and a balanced diet, is essential.
Question 3: Is there a specific type of heavy cream that is considered optimal for this beverage?
Heavy cream derived from grass-fed cows is often preferred due to its potentially higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA). However, any high-quality heavy cream, preferably organic and free from additives, is suitable.
Question 4: Can individuals with lactose intolerance safely consume coffee prepared with heavy cream?
Heavy cream contains lactose, although typically in smaller quantities than milk. Individuals with mild lactose intolerance may tolerate small amounts. Lactose-free heavy cream alternatives are also available.
Question 5: Does coffee prepared with heavy cream provide sustained energy throughout the day?
The combination of caffeine and fat may contribute to sustained energy levels. Caffeine provides an immediate stimulant effect, while fat offers a slower-releasing energy source. Individual responses may vary.
Question 6: Are there potential side effects associated with consuming coffee prepared with heavy cream?
Potential side effects include digestive discomfort, such as bloating or diarrhea, particularly with excessive consumption or in individuals with sensitive digestive systems. The high caloric content can also contribute to weight gain if not managed appropriately.
The integration of this beverage into a dietary regimen requires careful consideration of individual needs, tolerances, and overall health goals. Consultation with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is recommended for personalized guidance.
The subsequent section will delve into the various recipes of this beverage and alternative ingredients.
Heavy Cream Bulletproof Coffee
The preceding exploration of heavy cream bulletproof coffee has illuminated its multifaceted nature, encompassing aspects from satiety and ketogenesis to digestive impact and caloric load. This analysis underscores the beverage’s potential benefits and drawbacks, revealing its complex interaction with individual physiology and dietary context. The quality of ingredients, particularly the heavy cream itself, emerges as a critical factor influencing the overall outcome. Ultimately, the impact of this beverage extends beyond simple caffeine delivery, engaging with metabolic processes that demand informed consideration.
The sustained integration of heavy cream bulletproof coffee into a dietary regimen warrants careful assessment. Individual responses may vary significantly, necessitating attentive self-monitoring and potential adjustments to overall dietary strategies. While the beverage may offer benefits for certain individuals, it is not a universal solution. The responsibility rests with the individual to evaluate the totality of available information and consult with qualified healthcare professionals, ensuring alignment with personalized health objectives. Further rigorous research is necessary to fully delineate the long-term effects and refine evidence-based recommendations regarding this increasingly prevalent dietary practice.