Products marketed as additions to coffee, designed to enhance flavor and texture while providing an elevated level of protein, are increasingly common. These formulations often include ingredients such as whey protein concentrate, casein, or plant-based alternatives like soy or pea protein. As an example, a powdered product might contain a blend of non-dairy creamer base and whey protein isolate to deliver a creamy texture and a measurable protein boost to a cup of coffee.
The inclusion of protein in coffee creamers addresses a growing consumer demand for functional foods that offer convenience and nutritional benefits beyond basic caloric intake. This addition can contribute to increased satiety, support muscle maintenance, and provide a sustained release of energy throughout the morning. Historically, coffee creamers primarily focused on delivering fat and carbohydrates, but the modern emphasis on macronutrient balance has spurred the development of protein-enriched alternatives.
Therefore, a deeper examination into the specific types of protein used, their impact on the creamer’s performance in hot beverages, and the overall nutritional profile of these enhanced products is warranted. Subsequent discussions will explore the manufacturing processes involved, potential allergen concerns, and the regulatory landscape governing the labeling and marketing of these specialized coffee enhancements.
Considerations for Selecting Protein-Enriched Coffee Creamers
This section provides guidance on factors to consider when choosing coffee creamers fortified with protein, focusing on nutritional content, ingredients, and suitability for individual dietary needs.
Tip 1: Assess Protein Source. Examine the origin of the protein. Whey, casein, soy, and pea proteins each possess distinct amino acid profiles and digestibility characteristics. Choose a source aligned with personal protein requirements and any dietary restrictions.
Tip 2: Evaluate Sugar Content. Many flavored creamers contain added sugars. Prioritize options with low or no added sugars to minimize caloric intake and potential blood sugar fluctuations. Consider unsweetened varieties and add sweeteners independently.
Tip 3: Analyze Fat Composition. Assess the type and quantity of fats present. Saturated fats should be consumed in moderation. Look for options incorporating healthier fats such as monounsaturated or polyunsaturated fats from sources like plant-based oils.
Tip 4: Investigate Ingredient List. Scrutinize the ingredient list for artificial flavors, colors, and preservatives. Opt for creamers with minimal artificial additives and recognizable ingredients whenever possible.
Tip 5: Check for Allergens. Individuals with food allergies or sensitivities should carefully review the label for potential allergens, including dairy, soy, nuts, or gluten. Choose allergen-free alternatives as needed.
Tip 6: Consider Lactose Content. For lactose-intolerant individuals, explore lactose-free or plant-based coffee creamers fortified with protein. Enzyme-treated dairy versions may also be suitable.
Tip 7: Examine Calorie Count. Be mindful of the calorie count per serving. Frequent consumption of high-calorie creamers can contribute to weight gain over time. Choose options that align with daily caloric goals.
The selection of a protein-enriched coffee creamer should be a deliberate decision, factoring in individual dietary needs and preferences. Careful attention to protein source, sugar content, fat composition, and ingredient list can ensure a more informed and healthful choice.
Subsequent sections will address the potential benefits and drawbacks of incorporating protein-enhanced coffee creamers into a balanced diet, as well as explore various product options available in the market.
1. Protein Source
The protein source is a critical determinant of the nutritional profile, functional properties, and overall suitability of protein-enriched coffee creamers. The type of protein used significantly influences the creamer’s amino acid composition, digestibility, and potential allergenic properties. For example, whey protein, derived from milk, provides a complete amino acid profile, making it advantageous for muscle protein synthesis. However, its dairy origin renders it unsuitable for individuals with lactose intolerance or milk allergies. Conversely, soy protein, a plant-based alternative, offers a lactose-free and cholesterol-free option, but its amino acid profile is not identical to that of whey, and some individuals may have soy allergies.
The protein source also affects the creamer’s behavior in hot beverages. Solubility and heat stability are essential characteristics. Certain proteins, like some hydrolyzed whey protein isolates, exhibit excellent solubility and maintain their structural integrity at high temperatures, preventing clumping or precipitation in coffee. Other protein sources may require specific processing techniques to improve their dispersibility and prevent undesirable textural changes. Moreover, the protein source can impact the creamer’s flavor. Some proteins impart a distinct taste, which may necessitate the addition of masking agents or flavor enhancers to achieve a palatable final product. For example, pea protein, while a popular plant-based option, can sometimes contribute a slightly earthy or beany flavor.
In summary, the choice of protein source in coffee creamers is a multifaceted decision, balancing nutritional benefits, functional attributes, and potential drawbacks. A thorough understanding of the characteristics of various protein sources is essential for manufacturers to formulate products that meet the diverse needs and preferences of consumers. Careful consideration of factors such as amino acid profile, allergenicity, solubility, heat stability, and flavor impact is paramount in creating high-quality and consumer-acceptable protein-enriched coffee creamers.
2. Amino Acid Profile
The amino acid profile of protein-enriched coffee creamers is a critical factor determining their nutritional value and potential health benefits. The amino acid composition dictates the protein’s ability to support various physiological processes, including muscle protein synthesis, enzyme production, and immune function. Different protein sources incorporated into coffee creamers, such as whey, casein, soy, or pea protein, exhibit distinct amino acid profiles, thereby influencing the overall nutritional quality of the product. For instance, whey protein is known for its high concentration of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), which are particularly important for muscle recovery and growth. A coffee creamer using whey protein will, therefore, offer a higher concentration of BCAAs compared to one using a different protein source. Conversely, plant-based proteins may have limiting amounts of certain essential amino acids, potentially reducing their effectiveness in supporting protein synthesis if consumed as the sole protein source.
Understanding the amino acid profile is particularly relevant when evaluating the functional benefits of protein-fortified coffee creamers. If the primary goal is to increase satiety or support weight management, a balanced amino acid profile that includes adequate amounts of essential amino acids can promote a feeling of fullness and reduce subsequent food intake. In contrast, if the intention is to enhance post-exercise recovery, a creamer with a high BCAA content, characteristic of whey protein, might be more advantageous. Manufacturers of these products must carefully consider the target consumer and the desired functional outcome when selecting a protein source and formulating the product. Transparency regarding the amino acid profile on product labels allows consumers to make informed choices based on their individual nutritional needs and goals. The absence of this information can obscure the actual nutritional value of the creamer, potentially misleading consumers about its benefits.
In conclusion, the amino acid profile is an indispensable component of assessing the quality and effectiveness of protein-enriched coffee creamers. Variations in amino acid composition among different protein sources directly affect the creamer’s capacity to deliver specific nutritional benefits. Awareness of the amino acid profile empowers consumers to make informed decisions aligned with their dietary needs and health objectives. Furthermore, manufacturers have a responsibility to clearly communicate this information to ensure transparency and prevent misrepresentation of the product’s nutritional value, ultimately contributing to a more informed and health-conscious consumer base.
3. Solubility
Solubility is a critical factor in determining the efficacy and consumer acceptance of protein-enriched coffee creamers. The ability of the protein component to fully dissolve in hot coffee directly impacts the creamer’s texture, mouthfeel, and overall palatability. Inadequate solubility can lead to clumping, sedimentation, or a gritty texture, negatively affecting the sensory experience and potentially reducing consumer satisfaction. The type of protein used significantly influences its solubility characteristics. For example, hydrolyzed whey protein isolates generally exhibit superior solubility compared to less processed whey protein concentrates due to the smaller peptide size and reduced tendency to aggregate. Plant-based proteins, such as pea or soy protein, may require specific processing techniques, such as micronization or enzymatic modification, to enhance their solubility in aqueous solutions. Failure to achieve adequate solubility can result in a product that is perceived as lower quality, regardless of its nutritional profile. A real-world example involves a protein-enhanced creamer that utilizes a poorly soluble casein protein; upon addition to hot coffee, the creamer forms visible clumps, rendering it unappetizing and unusable, ultimately leading to product rejection.
The impact of solubility extends beyond the immediate sensory experience. Poorly soluble proteins may exhibit reduced bioavailability, meaning that the body is less able to absorb and utilize the amino acids they contain. This diminished bioavailability can negate some of the intended nutritional benefits of adding protein to the creamer. Furthermore, incomplete dissolution can affect the stability and shelf life of the creamer. Undissolved protein particles may promote microbial growth or undergo unwanted chemical reactions, leading to spoilage or a reduction in product quality over time. To address these challenges, manufacturers employ various techniques to improve protein solubility, including adjusting the pH of the creamer, adding emulsifiers or stabilizers, and using specialized processing methods to modify the protein structure. The selection of appropriate ingredients and processing parameters is essential for creating a protein-enriched coffee creamer that maintains its solubility and delivers its intended nutritional benefits throughout its shelf life.
In summary, solubility is a paramount attribute of protein-enriched coffee creamers, directly influencing their sensory appeal, nutritional value, and stability. Inadequate solubility results in negative sensory experiences, reduced protein bioavailability, and potential product degradation. Overcoming solubility challenges requires careful selection of protein sources and the implementation of appropriate processing techniques. By prioritizing solubility in the formulation and manufacturing process, producers can ensure that their protein-enriched coffee creamers meet consumer expectations and deliver the intended functional and nutritional advantages. This understanding also stresses the importance of transparent labeling, providing consumers with information about the type of protein used and any processing methods employed to enhance its solubility, enabling them to make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Flavor Impact
The addition of protein to coffee creamers invariably alters the flavor profile, presenting a significant challenge to formulators. Protein inherently possesses a taste distinct from traditional creamer components like fats and carbohydrates. This inherent flavor, which varies depending on the protein source (whey, casein, soy, pea, etc.), can manifest as bitterness, chalkiness, or a general off-flavor, affecting the overall palatability of the coffee. The extent of this impact depends on the concentration of protein, the type of protein processing employed, and the presence of masking agents or flavor enhancers. For instance, a creamer using a high concentration of unflavored whey protein concentrate might impart a noticeable dairy or “whey-like” taste, which some consumers find undesirable. Conversely, a creamer utilizing hydrolyzed whey protein isolate, which has undergone processing to reduce its inherent flavor, might exhibit a less pronounced flavor impact, albeit potentially at a higher cost.
Mitigating the negative flavor impact is a critical component of successful protein-enriched coffee creamer development. Manufacturers employ various strategies, including the use of flavor masking agents (e.g., vanilla, chocolate, caramel), sweeteners, and careful selection of protein sources. Flavor masking agents function by suppressing or covering the undesirable protein flavors, while sweeteners can balance the overall taste profile. For example, a creamer containing pea protein, known for its earthy flavor, might incorporate cocoa powder to create a chocolate-flavored product, effectively masking the pea protein’s inherent taste. Furthermore, the particle size and dispersibility of the protein can influence the perceived flavor. Smaller protein particles, which dissolve more readily, are less likely to contribute to a gritty or chalky texture, thereby reducing the negative flavor impact. The aroma profile is also influenced by the protein added, and its alteration can be a critical factor in consumer perception.
In conclusion, the flavor impact of protein addition is an intrinsic consideration in the formulation of coffee creamers. The inherent flavor of protein, its concentration, and processing methods all contribute to the final taste profile. Successful product development necessitates a strategic approach to flavor mitigation, employing masking agents, sweeteners, and optimizing protein characteristics. Understanding the interplay between protein type, concentration, processing, and flavoring agents is paramount in creating palatable and consumer-acceptable protein-enriched coffee creamers, highlighting the crucial balance between nutritional enhancement and sensory experience. The challenge remains to create a product that not only delivers functional benefits but also satisfies the taste preferences of a diverse consumer base.
5. Macronutrient Ratio
The macronutrient ratio, representing the proportions of protein, carbohydrates, and fats, is a fundamental aspect of any food product, including coffee creamers fortified with protein. This ratio significantly influences the product’s caloric density, satiety index, and impact on metabolic processes. Understanding the macronutrient ratio is essential for consumers seeking to align their dietary choices with specific health or fitness goals, and for manufacturers aiming to formulate products that meet evolving consumer demands.
- Caloric Contribution
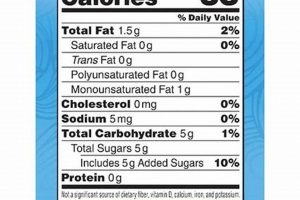
The macronutrient ratio dictates the overall caloric content of the coffee creamer. Protein and carbohydrates provide approximately 4 calories per gram, while fats contribute about 9 calories per gram. A creamer with a higher fat content will inherently possess a greater caloric density compared to one with a higher protein content, assuming equal serving sizes. For individuals monitoring their caloric intake for weight management, selecting a protein-enriched creamer with a lower fat content can be a strategic choice. For instance, a creamer comprised of 5 grams of protein, 2 grams of carbohydrates, and 3 grams of fat would yield approximately 55 calories, while a creamer with 2 grams of protein, 2 grams of carbohydrates, and 7 grams of fat would contain approximately 79 calories.
- Satiety and Appetite Regulation
The macronutrient ratio influences satiety, the feeling of fullness and satisfaction after consuming a food product. Protein, compared to carbohydrates and fats, is generally considered the most satiating macronutrient. By increasing the protein content relative to carbohydrates and fats, a coffee creamer can potentially contribute to increased satiety, leading to reduced overall caloric consumption throughout the day. For example, a creamer with a high protein-to-fat ratio may help suppress appetite and reduce the urge to snack between meals, particularly in the morning. This can be beneficial for individuals seeking to manage their weight or control cravings.
- Metabolic Impact
The macronutrient ratio can affect metabolic processes, including blood sugar regulation and insulin response. Carbohydrates, particularly simple sugars, tend to elicit a more rapid increase in blood glucose levels compared to protein and fats. A creamer with a high carbohydrate content may lead to a spike in blood sugar followed by a subsequent crash, potentially resulting in energy fluctuations and increased hunger. In contrast, a creamer with a higher protein content and lower carbohydrate content may promote more stable blood sugar levels, providing a sustained release of energy. This is particularly relevant for individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance who need to carefully manage their blood sugar levels.
- Impact on Nutrient Density
The macronutrient ratio can directly influence the nutrient density of the creamer. Nutrient density refers to the concentration of essential vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds relative to the caloric content of the product. A creamer with a favorable macronutrient ratio, such as a high protein-to-fat ratio, can provide a greater amount of essential nutrients per calorie compared to a creamer with a less optimal ratio. For example, a creamer fortified with vitamins and minerals in addition to a high protein content can offer a more nutrient-dense option compared to a creamer primarily composed of fat and sugar.
The macronutrient ratio of protein-enriched coffee creamers is a multifaceted consideration that impacts caloric intake, satiety, metabolic processes, and nutrient density. Consumers can utilize this information to make informed choices aligned with their dietary goals, while manufacturers can leverage this knowledge to formulate products that meet the diverse needs and preferences of the marketplace. A thorough understanding of the interplay between macronutrient ratios and health outcomes is essential for both consumers and producers alike, ensuring responsible and effective product development and utilization.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses commonly encountered inquiries regarding protein-enriched coffee creamers, providing concise and factual information to aid in understanding their composition, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
Question 1: Is coffee creamer protein an effective way to supplement protein intake?
Coffee creamer protein can contribute to daily protein intake, but its effectiveness depends on the amount consumed and the protein source. It should not be considered a primary protein source but rather a supplementary one. A balanced diet remains crucial for meeting overall protein requirements.
Question 2: Are there any potential side effects associated with consuming coffee creamer protein?
Potential side effects vary depending on the protein source and individual sensitivities. Dairy-based protein sources may cause digestive issues in lactose-intolerant individuals. Excessive protein intake, regardless of the source, can lead to digestive discomfort or kidney strain in susceptible individuals. A review of ingredients and potential allergens is advised.
Question 3: Does coffee creamer protein alter the taste of coffee?
The addition of protein can influence the taste of coffee. The extent of alteration depends on the protein source, concentration, and presence of flavoring agents. Some individuals may detect a subtle difference in taste or texture, while others may find it imperceptible. Experimentation with different brands and flavors is recommended to find a palatable option.
Question 4: Is coffee creamer protein suitable for individuals with dietary restrictions?
Suitability depends on the specific dietary restriction and the ingredients used in the creamer. Individuals with lactose intolerance should opt for dairy-free alternatives. Those with soy allergies should avoid soy-based creamers. Careful examination of the ingredient list is essential to ensure compatibility with individual dietary needs.
Question 5: How does coffee creamer protein compare to other protein supplements?
Coffee creamer protein provides a relatively small amount of protein per serving compared to dedicated protein supplements like powders or bars. It is primarily intended as a convenient addition to coffee rather than a substantial source of protein. Individuals with significant protein needs should consider more concentrated protein supplements.
Question 6: What is the best way to store coffee creamer protein?
Storage recommendations vary depending on the type of creamer. Powdered creamers should be stored in a cool, dry place in an airtight container to prevent clumping and maintain freshness. Liquid creamers typically require refrigeration after opening. Adherence to the manufacturer’s instructions is crucial for preserving product quality.
In summary, protein-enriched coffee creamers offer a convenient way to supplement protein intake, but potential side effects, taste alterations, and suitability for dietary restrictions must be considered. Careful examination of ingredients and individual needs is essential before incorporating these products into the diet.
Subsequent sections will delve into the regulatory aspects surrounding the production and labeling of protein-enriched coffee creamers, as well as explore future trends in this evolving market segment.
Conclusion
This exploration has illuminated the multifaceted aspects of coffee creamer protein, encompassing its nutritional composition, functional attributes, and potential impact on consumer health and sensory experience. The protein source, amino acid profile, solubility, flavor influence, and macronutrient ratio each contribute significantly to the overall quality and acceptability of these products. Understanding these factors empowers both manufacturers and consumers to make informed decisions regarding formulation, selection, and utilization.
Moving forward, continued research and development are essential to optimize the nutritional profile, enhance palatability, and address potential allergen concerns associated with coffee creamer protein. Transparency in labeling and responsible marketing practices are crucial for fostering consumer trust and ensuring that these products contribute positively to dietary habits and overall well-being. The future trajectory of this market segment hinges on a commitment to innovation, scientific rigor, and a dedication to meeting the evolving needs of a health-conscious populace.