The composition of a popular flavored, non-dairy creamer includes water, corn syrup solids, vegetable oil (partially hydrogenated coconut or palm kernel, hydrogenated soybean), and less than 2% of sodium caseinate (a milk derivative), dipotassium phosphate, mono- and diglycerides, artificial flavors, carrageenan, sucralose, and acesulfame potassium.
Understanding the specific components is important for individuals managing dietary restrictions, allergies, or those seeking to make informed choices about the products they consume. The formulation offers a shelf-stable, convenient alternative to dairy cream, delivering a distinctive taste profile to enhance coffee or other beverages. The presence of emulsifiers and stabilizers ensures a consistent texture and prevents separation.
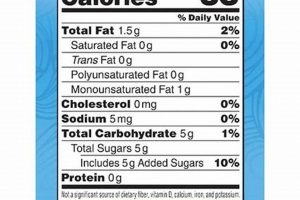
A detailed examination of food product labels provides valuable insight into the various substances that contribute to its overall sensory experience and functional properties, allowing consumers to better understand their nutritional intake and potential health implications.
Considerations Regarding Composition
The following points provide a structured understanding of aspects related to a flavored, non-dairy creamer’s constituents. They are intended to inform rather than prescribe.
Tip 1: Evaluate Sweetener Content: Observe the presence of corn syrup solids, sucralose, and acesulfame potassium. Individuals monitoring sugar or artificial sweetener intake should consider the implications for their dietary needs.
Tip 2: Assess Fat Sources: Acknowledge the inclusion of partially hydrogenated vegetable oils. Awareness of the type and processing method of oils is relevant for those tracking fat consumption.
Tip 3: Identify Potential Allergens: Note the presence of sodium caseinate, a milk derivative. Lactose-intolerant individuals or those with milk allergies must exercise caution.
Tip 4: Understand Additives: Recognize the presence of dipotassium phosphate, mono- and diglycerides, and carrageenan. Researching the roles of these additives in food processing is advisable.
Tip 5: Account for Artificial Flavors: Realize that artificial flavors are used. Consumers sensitive to artificial flavorings should be aware of their inclusion.
Tip 6: Portion Control Awareness: Due to the concentrated nature of the product, moderate serving sizes are important for managing caloric and compositional intake.
Tip 7: Compare Nutritional Information: Scrutinize nutritional facts panels when comparing different brands or flavors. This informs comparative analyses of various constituents.
Understanding the components of the product permits a more informed approach to its consumption, factoring in individual dietary requirements and preferences.
The subsequent section will explore alternative creamer options, offering a contrast to the previously discussed formulation.
1. Sweeteners
Sweeteners constitute a principal component in the formulation of coffee creamers, significantly influencing the overall taste profile and contributing to caloric content. Their presence and type merit careful evaluation, especially for individuals managing specific dietary requirements.
- Corn Syrup Solids
Corn syrup solids, derived from corn starch, function as a bulk sweetener, adding volume and sweetness. These solids consist of glucose molecules. Their inclusion contributes to the overall carbohydrate content and glycemic index of the creamer, aspects relevant for individuals monitoring blood sugar levels or carbohydrate intake.
- Sucralose
Sucralose is an artificial sweetener that provides significant sweetness without contributing substantially to caloric intake. It is derived from sugar but is not metabolized in the same way. The presence of sucralose allows for a reduction in the quantity of corn syrup solids required, potentially impacting the overall caloric density of the creamer.
- Acesulfame Potassium (Ace-K)
Acesulfame potassium, another artificial sweetener, often complements sucralose in formulations. It contributes sweetness and enhances the overall flavor profile. Similar to sucralose, Ace-K provides minimal calories and serves to reduce reliance on sugar-based sweeteners. Its safety profile has been evaluated by regulatory agencies.
- Impact on Sweetness Profile
The combination of corn syrup solids, sucralose, and acesulfame potassium creates a complex sweetness profile. The corn syrup solids provide a foundational sweetness, while sucralose and Ace-K intensify the perceived sweetness. The ratio of these sweeteners is carefully calibrated to achieve a palatable and consistent taste, ensuring a satisfying experience for the consumer.
The type and quantity of sweeteners employed directly impact the nutritional profile and consumer acceptance of the creamer. Understanding the roles of individual sweetening agents allows for more informed decisions regarding product selection and consumption.
2. Vegetable Oils
Vegetable oils constitute a crucial component, significantly influencing texture and stability. The specific oils employed, often partially hydrogenated coconut, palm kernel, or hydrogenated soybean oil, contribute to the creamy mouthfeel and extended shelf life characteristic of this product. Partial hydrogenation, though decreasingly prevalent, converts liquid oils into semi-solid fats at room temperature, enhancing the product’s consistency. The selection of these oils reflects a balance between cost, functionality, and sensory properties. The presence of these fats influences the overall fat content, an important consideration for those monitoring dietary intake.
The choice of vegetable oil also impacts the fatty acid profile. Coconut and palm kernel oils are relatively high in saturated fats, which may be a relevant factor for individuals concerned about cardiovascular health. Soybean oil, when hydrogenated, undergoes changes that affect its fatty acid composition, including the potential formation of trans fats. The formulation, therefore, is subject to evolving nutritional guidelines and consumer preferences, prompting ongoing reformulation efforts by manufacturers to optimize the balance between taste, texture, and health considerations. The sourcing and processing of these oils are aspects increasingly scrutinized for environmental sustainability and ethical production practices.
In summary, the inclusion of vegetable oils directly shapes the physical and nutritional properties of this coffee enhancer. Awareness of the type, processing method, and fatty acid profile of these oils is essential for consumers aiming to make informed choices aligned with their dietary needs and health goals. The ongoing evaluation of these oils reflects the evolving understanding of their impact on human health and environmental sustainability.
3. Milk Derivative
The inclusion of a milk derivative within the formulation of a non-dairy creamer warrants specific attention due to its implications for individuals with lactose intolerance or milk allergies. This component, typically sodium caseinate, introduces a level of complexity in product classification and consumer suitability.
- Sodium Caseinate Composition
Sodium caseinate is a protein derived from milk. It is created by extracting casein from milk and converting it into a soluble form using sodium hydroxide. While processing reduces lactose levels, trace amounts may persist. Individuals with severe milk allergies should exercise caution, as even minimal quantities can trigger adverse reactions.
- Functional Role
Sodium caseinate serves as an emulsifier, stabilizing the creamer’s texture and preventing separation of its constituent parts. It enhances the product’s ability to blend smoothly into coffee or other beverages. Its presence contributes to the creamy mouthfeel desired by consumers.
- Labeling Implications
The presence of sodium caseinate necessitates accurate product labeling. Despite being marketed as a non-dairy alternative, its inclusion mandates disclosure to alert consumers with milk-related sensitivities. This labeling enables informed purchasing decisions and promotes consumer safety.
- Alternative Formulations
Recognizing the limitations posed by sodium caseinate, manufacturers are exploring alternative emulsifiers and stabilizers to create truly dairy-free creamer options. These formulations often utilize plant-based proteins or gums to achieve similar functional properties without introducing milk-derived components.
The incorporation of a milk derivative, specifically sodium caseinate, in a non-dairy creamer represents a trade-off between functional performance and inclusivity for consumers with dietary restrictions. Understanding its presence, role, and implications is critical for those making informed choices about product selection.
4. Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers play a crucial role in maintaining the stability and texture of flavored creamers. Within the composition of this product, substances such as mono- and diglycerides act as emulsifying agents, preventing the separation of oil and water-based components. Without these emulsifiers, the creamer would exhibit phase separation, resulting in an undesirable appearance and inconsistent flavor distribution. This functionality is paramount for achieving the homogenous consistency expected by consumers. For example, in the absence of mono- and diglycerides, the vegetable oils would separate from the water and other ingredients, forming an oily layer on top, a phenomenon readily observable in homemade salad dressings that lack emulsifiers.
The effectiveness of emulsifiers is determined by their molecular structure, possessing both hydrophilic (water-attracting) and lipophilic (oil-attracting) properties. This dual affinity allows them to position themselves at the interface between oil and water, reducing surface tension and facilitating the formation of a stable emulsion. Furthermore, emulsifiers contribute to the creamer’s shelf life by inhibiting microbial growth and preventing oxidative degradation. For instance, carrageenan, while primarily a stabilizer, also exhibits some emulsifying properties, adding to the overall structural integrity of the product. The specific combination and concentration of emulsifiers are carefully optimized to achieve the desired texture, stability, and sensory attributes.
In summary, emulsifiers are indispensable for the physical characteristics and long-term quality of the final product. Their presence ensures a uniform, palatable coffee enhancing experience. The technological significance of emulsifiers extends beyond mere aesthetics, contributing to the overall stability and preventing undesirable changes during storage and use. The selection and application of these agents are critical for achieving the desired attributes and meeting consumer expectations.
5. Artificial Flavors
Artificial flavors constitute a significant component of flavored creamers, providing a cost-effective and consistent means of imparting specific taste profiles. Their utilization raises considerations regarding consumer perception and dietary choices. The presence and nature of these substances warrant careful examination.
- Chemical Composition and Production
Artificial flavors are created through the synthesis of various chemical compounds in a laboratory setting. These compounds are designed to mimic the taste of natural substances, such as hazelnut. The production process involves manipulating organic molecules to replicate the sensory properties of the target flavor. These substances are subject to regulatory oversight to ensure safety and adherence to established standards.
- Sensory Impact and Consumer Expectations
The inclusion of artificial flavors aims to deliver a consistent and palatable taste experience. The hazelnut flavoring is designed to replicate the characteristic nutty and slightly sweet notes of natural hazelnuts. Consumer expectations play a pivotal role in shaping the formulation, with manufacturers striving to achieve a flavor profile that resonates positively with target demographics. The use of artificial flavors enables the attainment of a uniform taste across batches and geographic locations.
- Labeling Requirements and Transparency
Regulatory frameworks mandate clear labeling of artificial flavors on product packaging. This requirement aims to provide consumers with transparent information regarding the composition. While the specific chemical compounds are typically not disclosed, the general designation “artificial flavor” must be prominently displayed. Enhanced transparency allows consumers to make informed decisions based on their individual preferences and dietary considerations.
- Cost Considerations and Formulation Choices
The utilization of artificial flavors presents a cost-effective alternative to natural extracts or flavorings. The economic advantage facilitates the production of affordable flavored creamers, appealing to a broad consumer base. Formulation choices are influenced by cost constraints, stability considerations, and the desired intensity of the hazelnut flavor. The selection process involves a balance between economic viability and sensory performance.
The application of artificial flavors in the product reflects a strategic decision aimed at achieving a specific taste profile while adhering to cost and regulatory constraints. Understanding the composition, sensory impact, and labeling requirements associated with these substances empowers consumers to make informed choices aligned with their individual needs and preferences.
Frequently Asked Questions About Ingredients in Coffee Mate Hazelnut Creamer
This section addresses common queries regarding the compositional makeup of this coffee enhancing product, providing clarity and factual information.
Question 1: Is this product truly dairy-free, given the presence of sodium caseinate?
The product is labeled as non-dairy; however, it contains sodium caseinate, a milk protein. This makes it unsuitable for individuals with milk allergies. While the lactose content is reduced during processing, it may not be appropriate for those with severe lactose intolerance. Individuals should review ingredient labels carefully.
Question 2: What is the function of partially hydrogenated oils, and are they a health concern?
Partially hydrogenated oils were previously used to enhance texture and shelf life. However, due to health concerns related to trans fats, manufacturers have largely reduced or eliminated them. The product formulation should be reviewed for current oil composition.
Question 3: What are “artificial flavors” comprised of, and are they safe for consumption?
Artificial flavors are complex mixtures of chemical compounds synthesized to mimic natural flavors. Regulatory bodies like the FDA deem approved artificial flavors safe for consumption at specified levels. However, individuals with sensitivities may react differently.
Question 4: What is the purpose of carrageenan, and are there potential side effects?
Carrageenan is a seaweed-derived ingredient used as a stabilizer and thickening agent. Some studies have suggested potential gastrointestinal side effects in sensitive individuals, but regulatory agencies consider it safe at typical usage levels.
Question 5: Why are multiple sweeteners, such as corn syrup solids and sucralose, used in combination?
The combination of sweeteners aims to achieve a desired sweetness profile and manage caloric content. Corn syrup solids provide bulk and sweetness, while sucralose is a high-intensity sweetener used in smaller quantities. This blend helps optimize taste while minimizing calorie contribution.
Question 6: How does the vegetable oil content impact the overall nutritional value?
The vegetable oil content contributes to the fat content, primarily saturated and potentially trans fats, depending on the specific oils used and their processing. This impacts the overall caloric density and fatty acid profile, factors to consider for dietary management.
Understanding the composition of this coffee enhancer through these frequently asked questions allows for informed consumer decisions, taking into account individual dietary needs and preferences.
The following section explores alternative creamer options with different ingredient profiles.
Conclusion
This exploration of the composition has illuminated the diverse components within this popular coffee enhancer. The presence of sweeteners, vegetable oils, a milk derivative, emulsifiers, and artificial flavors collectively defines the product’s sensory attributes and functional properties. A comprehensive understanding of these substances enables consumers to make informed choices aligned with individual dietary requirements and health considerations.
Continued scrutiny of product labeling and ongoing research into alternative formulations remain critical. The evolving landscape of food science and consumer awareness necessitates a proactive approach to understanding and evaluating the ingredients in commonly consumed products. Further investigation into the long-term health implications of specific additives warrants sustained attention and rigorous scientific inquiry.